Jennifersoft’s references have been proven in the cloud environment.

Support Cloud
Jennifersoft has one of the largest customer and reference pools of APM in the domestic cloud environment. The company has proven its scalability and reliability with a major cloud provider, such as AWS and AZURE, which run one of the biggest servers.
Jennifersoft has provided a variety of support on the cloud, ranging from installation in a cloud environment, the scalability and reliability of the agent/server, the monitoring perspective of the cloud, and the license system in the business area.

Jennifersoft’s references have been proven in the cloud environment.
The company has numerous references using JENNIFER in the cloud. Its monitoring feature has been working well at Samsung Electronics and EBay, which have large-scale traffic. Moreover, Jennifersoft was able to respond promptly by expanding in real time when customers rushed to make purchases in a flash sale. You can see a detailed example of the start-up below.
Service operator of Fanmaum
“It was really simple to use JENNIFER. I installed the remote agent, generated AMI, and added them to the Auto-Scale group. After that, I was able to use the monitoring service as it was automatically connected once the machine was launched. (I have tried multiple log analysis tools before; however, JENNIFER is the best tool in terms of easy installation and usage. Also, it was helpful for checking the trouble point in real time, frequently calling files, and lead time per transaction.)”
– Fanmaum(Startup company in korea)
: https://cdn.jennifersoft.com/wp-content/uploads/Documents/ko/JENNIFER+CASESTUDY_FANMAUM_EN.pdf
Classting service operator
“Classting controls the number of servers depending on the amount of usage by using the Auto-Scaling of AWS. We are also monitoring the Classting to see if it works properly with AWS Cloud Watch. Due to the characteristic of the service, high traffic could occur instantly. It was hard to control traffic as AWS Cloud Watch reports such instances one minute late instead of in real time. JENNIFER, however, allowed us to report in real time. We were able to respond to problems in a timely manner.”
– Classting(Startup company in korea)
: https://cdn.jennifersoft.com/wp-content/uploads/Documents/ko/JENNIFER+CASESTUDY_CLASSTING_EN.pdf
Installing Agents in Cloud and Container Environments According to Jennifer Cloud environment, we provide the following ‘How to’ documents.
Cloud environment
– All kinds of IaaS (same as existing installation method) in Cloud environment
Docker and Docker-based containers
– Kubernetes (same as Docker)
– OpenShift
: https://edu.jennifersoft.com/articles/jennifer-5/java-agent-5/using-jennifer-with-red-hat-openshift
Expandable architecture and integrated management
One of the major features of Cloud is scalability. In other words, the service needs to allow users to control the number of servers in accordance with the number of transactions regardless of the hardware specifications.
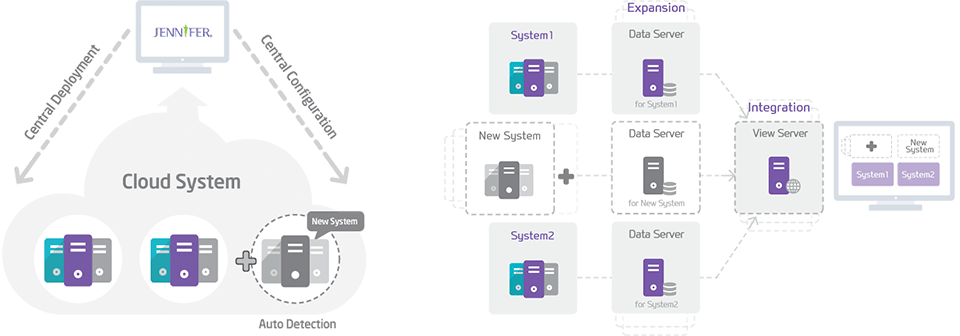
In this environment, the managing cost of monitoring would become too high if users have to install agents every time each server conducts scaling (scale in/out). JENNIFER offers the following features to fix this issue.
- Auto-detection in Scale In/Out Instance
- Auto-renew ID during an instance of identical ID access
- Auto-delete an unused instance from a monitoring target
- Integrated agent/server management (batch release and upgrade)
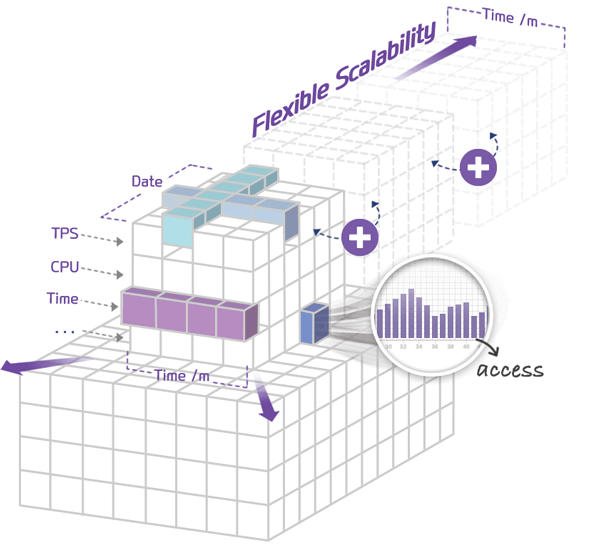
Processing large-capacity server and saving data
JENNIFER Repository is designed as architecture with flexible scalability. Using the repository, users are able to save large-capacity performance data rapidly and conduct comparative analysis. They can also reduce extra costs for building a database on the system.
Integrated monitoring from task perspective
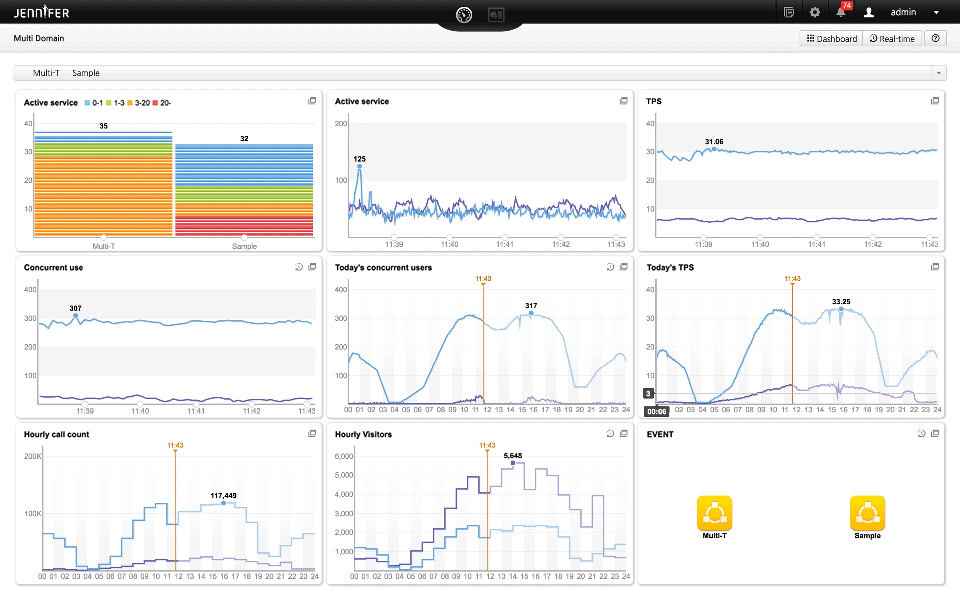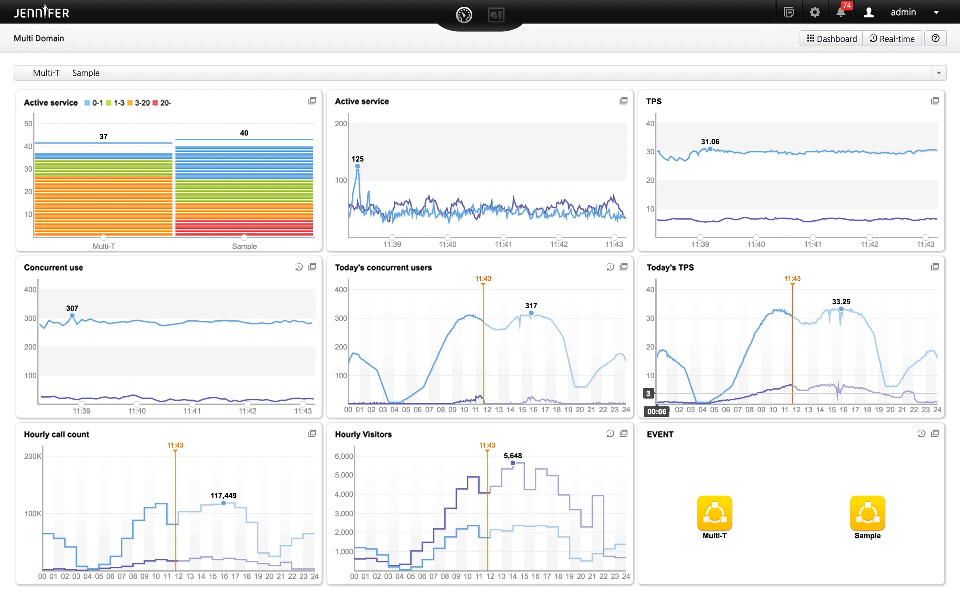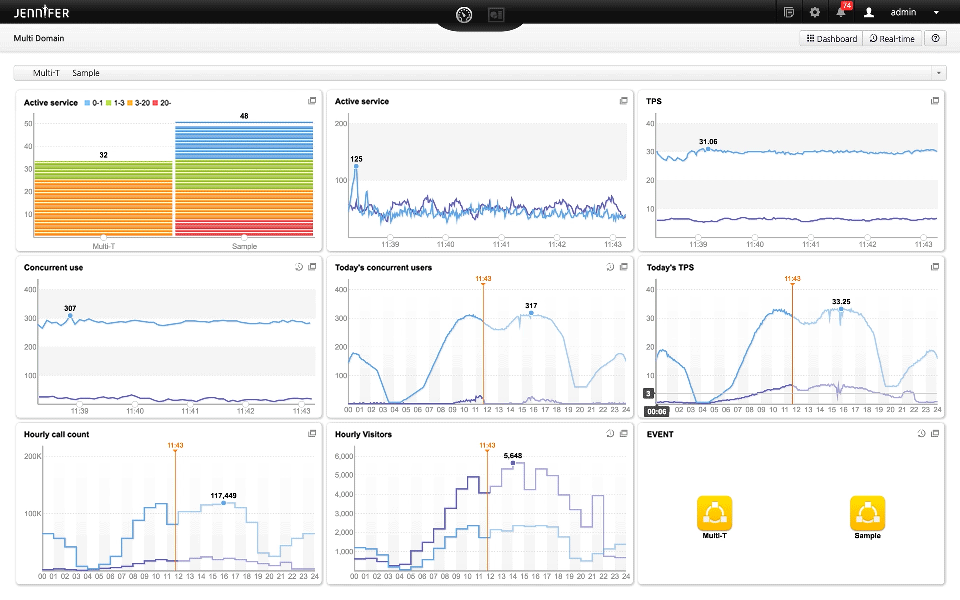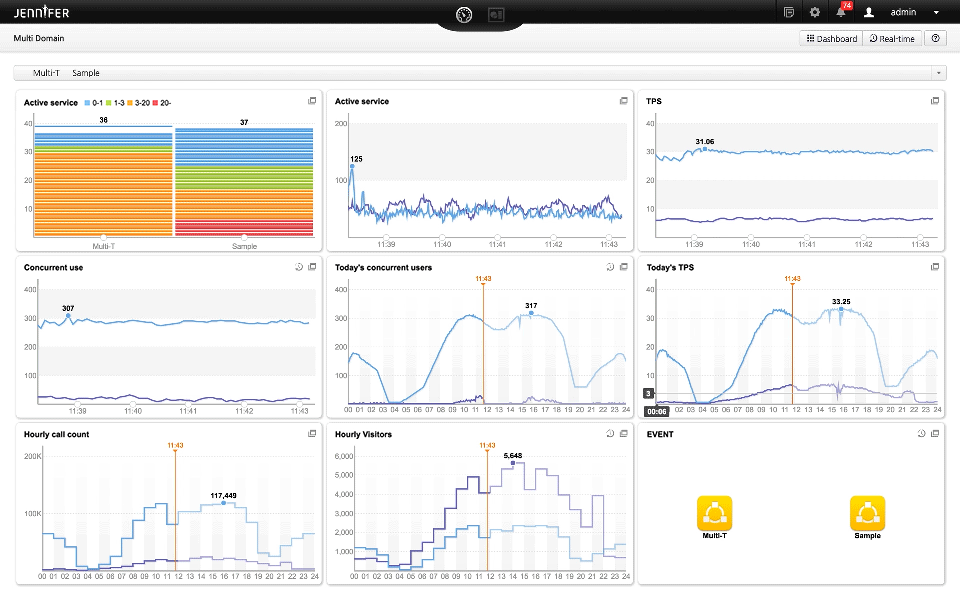
Integrated monitoring (called Domain at Jennifersoft) is highly effective in the cloud environment, where scale in/out occurs frequently, rather than monitoring individual instances.
You can monitor the change through Multi-Domain Dashboard at once.
Monitoring the number of changes of ongoing instances in real time is sufficient to see how scale in/out is occurring rather than focusing on its performance.
